

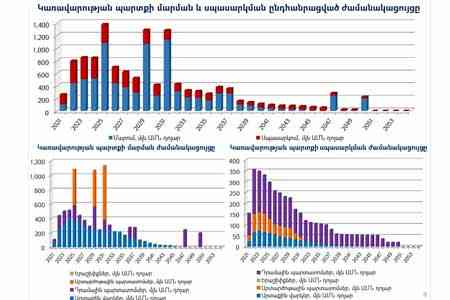
ArmInfo.According to the data of the RA Ministry of Finance, in 2025, Armenia will have to send almost $ 1.4 billion for the government debt repayment and services (excluding the debt of the Central Bank of Armenia), formed at the end of August 2021.
According to the presented data, the state debt of the Republic of Armenia from $ 7 billion 968.5 million, formed by December 31, 2020, grew by about $ 990 million and reached $ 8 billion 953 million by August 31 of this year. Compared to the end of 2020, the figure increased by 6.09%, and compared to the same period last year - by about 19.6%. Meanwhile, according to the forecasts laid down in the basis of the state budget for the current year, as of December 31, 2021, the government debt was planned at around 4.522 billion drams or $ 8.551 billion - 66% of GDP.
In January-August 2021, the government debt increased from $ 7 billion 508.5 million (by the end of 2020) to $ 8 billion 485 million - by about $ 976 million, or 6.71%. External debt (debt obligations of Armenia to international organizations and foreign states, funds received from the emission of Eurobonds) from $ 5 billion 599.5 million to $ 6 billion 185.1 million - for $ 586 million. In particular, on January 26 this year, Armenia placed among international investors the 4th issue of 10-year debt securities in the amount of $ 750 million.
The established annual yield on bonds of the 4th issue turned out to be lower than the yield on the 3rd issue - 3.875% versus 4.625%. During the reporting period, domestic debt increased from $ 1 billion 909.0 million by about $ 391 million to $ 2 billion 299.8 million. The Central Bank's debt amounted to $ 468 million (from $ 495.5 million by the end of last year, it decreased by 3.95%).
At present, in the structure of government debt, 75.6% are debt obligations in foreign currency.
Meanwhile, over its almost 28-year history (since Armenia gained independence), the Republic of Armenia has attracted borrowings in the amount of about $ 6.8 billion, and over the past three years "managed" to increase the national debt by almost $ 2 billion 100 million. At the end of December 2017, the total public debt of Armenia reached $ 6.774 billion, and by the time the new government was formed, at the end of April 2018, this figure was $ 6,867 billion. By the end of 2018, the public debt increased to $ 6,922 billion, in 2019 - to $ 7 321 billion. By the end of 2020, the national debt increased by $ 647 million. - up to $ 7.968 billion, of which $ 7.509 billion is government debt (external debt - $ 5.593 billion, and domestic debt - $ 1.915 billion).
As a result, if the ratio of government debt to GDP by the end of 2019 was 49.9%, then by the end of 2020 the level of government debt to GDP reached 63.5%. Thus, Armenia has "gone" beyond the limits established by the republic's fiscal rules, which allow the indicator to grow up to 60% of GDP. Currently, the ratio of government debt to GDP is 62.3%.
The national debt is stable and manageable! Ministry of Finance of Armenia assures!
As head of the Macroeconomic Policy Department of the RA Ministry of Finance Eduard Hakobyan stated on the air of Public Television, the annual comprehensive diagnostics of debt risks shows that, despite the increase in the debt burden that occurred during the crisis period (pandemic, war in Artsakh, Ed. note), the reaction of the financial authorities was adequate to the existing conditions. "As estimates show, debt is still in the area of manageability and stability," he said.
Representative of the legislative branch, the head of the Standing Committee on Financial, Credit and Budgetary Issues of the National Assembly Gevorg Papoyan, in turn, said on the air of Public Television that in the conditions of war and a pandemic Armenia could follow the path of massive cost cuts, or pursue a stimulating fiscal policy, then there is - to carry out the main expenses, filling the gap with credit resources. The government, according to him, chose the second path, since the first led to a greater economic recession (at the end of 2020, Armenia recorded a decline in GDP of 7.4%, Ed. note). More important is how effectively and in what directions the borrowings were spent, Papoyan said, pointing out that large sums were invested in fixed assets, which in the long term promises the country economic growth and, consequently, the ability to painlessly service the state debt.
At the same time, according to the representative of the Ministry of Finance, the framework established by the RA law is very flexible - in crisis conditions it allows one to deviate in a certain way, and after making a number of adjustments to the current policy, to return to a given channel. In particular, over the next 5 years, the Ministry of Finance plans not only to return to the permissible limits, but also to reach the mark of 54% of GDP.
The beauty of a debt is its payment
As ArmInfo previously reported, referring to the Strategic Program for Government Debt Management for 2022-2024, it is until the moment of payments on the state debt in 2025 that Armenia plans to carry out the next and fifth tranche of Eurobonds in the international market in 2024. The funds received from the emission of Eurobonds will be used to buy back bonds of 2025 maturity. Meanwhile, as evidenced by the data of the RA Ministry of Finance on the schedule of repayment and servicing of government debt until 2053, the state budget of Armenia is to be "tested for strength" both in 2025 and in 2029 and 2031. Then the financial system of the republic will have to "lay out" about $ 1.3 billion.
Lenders have a good memory:
In January-August of this year alone, 104.2 billion drams were allocated to pay interest rates on the government debt.
The largest creditor of Armenia at present is the World Bank - the share of the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development and the International Development Association accounts for 38.7% of the state debt of the Republic of Armenia. The second major creditor is the Asian Development Bank - 16.9%, the third position is held by the International Monetary Fund - 7.5%, followed by the Eurasian Development Bank with 7.1% and the European Investment Bank - 2.9%.
Among the large creditor countries of Armenia, the Russian Federation is in first place - 7.1% of the public debt, Germany - 6.1%, France - 3.2%, Japan - 4.6%, China - 0.5%, the United States - 0 .3%, Development Bank of Abu Dhabi - 0.1%.